Documentation for v4.0. Some new links, images etc.
Showing
- LICENSE 1 addition, 1 deletionLICENSE
- README.md 2 additions, 2 deletionsREADME.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/Changelog.md 1 addition, 0 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/Changelog.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/Examples.md 21 additions, 18 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/Examples.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/FAQ.md 9 additions, 7 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/FAQ.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/Introduction.md 27 additions, 22 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/Introduction.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/Links.md 0 additions, 3 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/Links.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/SDT Build System Components and Licenses.md 3 additions, 3 deletions...chema4.0/docs/SDT Build System Components and Licenses.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/SDT Build System.md 10 additions, 9 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/SDT Build System.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/SDT_Components.md 209 additions, 197 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/SDT_Components.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/SDT_JSON.md 100 additions, 95 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/SDT_JSON.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/SDT_UML.uxf 139 additions, 139 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/SDT_UML.uxf
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/UML Diagram.md 6 additions, 0 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/UML Diagram.md
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/images/MC.Action.DataPoint.Event.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/images/MC.Action.DataPoint.Event.png
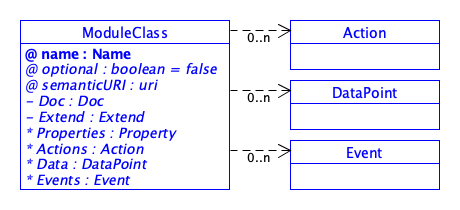
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/images/ModuleClass.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/images/ModuleClass.png
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/images/SDT_UML_Basic_Elements.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/images/SDT_UML_Basic_Elements.png
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/images/SDT_simplified.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/images/SDT_simplified.png
- SDT/schema4.0/docs/images/SubDevice.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSDT/schema4.0/docs/images/SubDevice.png
| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:






